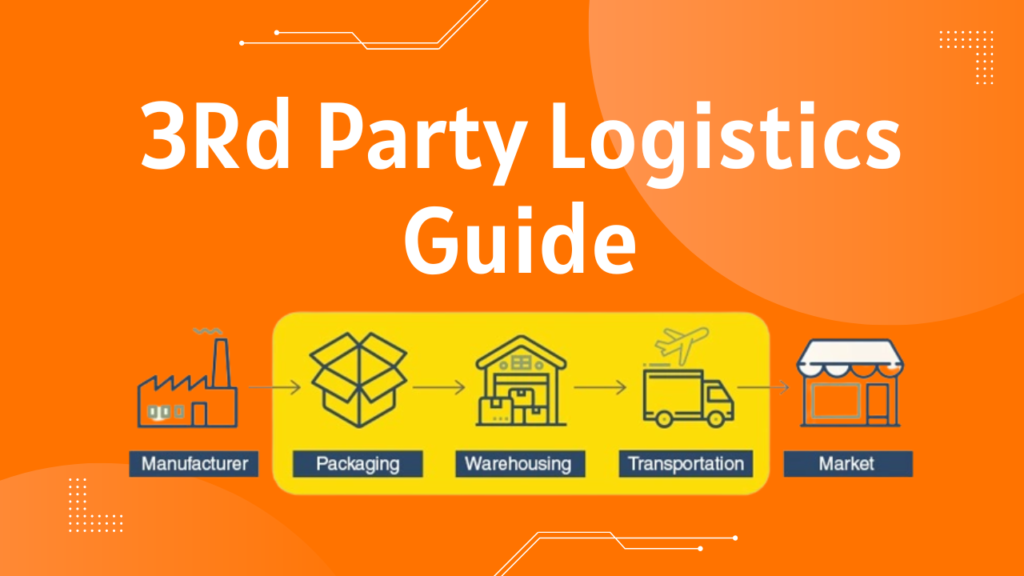
The Ultimate 3PL Guide: Everything You Need to Know About Third-Party Logistics
For e-commerce business owners, order fulfillment is a critical aspect of their operations. However, as the business expands, managing order fulfillment in-house may become impractical.
This is where third-party logistics (3PL) comes in. In this guide, you’ll learn all about 3PL and how it can help your business.
What are third-party logistics (3PLs)?
3LP stands for “Third-Party Logistics.” It refers to the outsourcing of logistics and supply chain management functions to a third-party provider.
The Ultimate 3PL Guide is a comprehensive resource that explains everything you need to know about third-party logistics, including its benefits, how it works, and the different types of services that 3PL providers offer.
It can help you gain a better understanding of 3PL and determine if it’s the right solution for your logistics needs.
The rise of e-commerce in the 1990s and 2000s led to the widespread adoption of the term 3PL and the expansion of 3PL services. Today, third-party logistics refers to the integration of warehousing and transportation services in supply chain management.
What a 3PL is Not?
A 3PL is not a warehouse that only serves one company. These types of warehouses are owned and run by the company that owns the products being stored.
They use software that is specific to their own business, which can make it difficult to manage inventory and billing for other companies. If a private warehouse wants to make money by storing goods for other companies, it may need to invest in a different software system.
What are the basic types of 3PL firms?
Transportation-based 3PLs
These companies offer transportation services, including freight forwarding, carrier management, and shipment tracking.
responsible for managing the shipment of inventory between manufacturers and their clients’ warehouses, as well as between their clients and their customers. This can involve working with freight forwarders who transport large shipments internationally, as well as small parcel shippers like UPS, FedEx, and USPS for domestic deliveries.
In addition to transportation, 3PLs may offer a variety of other services such as warehousing, order fulfillment, and inventory management. They may also provide value-added services such as packaging, labeling, and kitting to meet specific customer needs.
Warehouse-based 3PLs
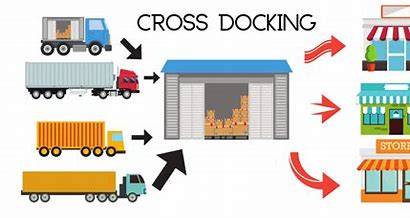
These companies provide warehousing and distribution services, including inventory management, order fulfillment, and cross-docking.
One of the most common types of 3PL providers is those that offer warehousing, fulfillment, and distribution services. This type of 3PL provides a wide range of basic fulfillment services, including storage, pick and pack, shipping, and returns management. Many sellers choose to work with this type of 3PL to outsource most, if not all, of their warehousing and fulfillment needs.
In addition to these core services, 3PL providers that offer warehousing, fulfillment, and distribution often also manage their clients’ transportation needs. This includes identifying which shipping carriers to use for each shipment, as well as managing the logistics of getting products from the warehouse to their final destination.
Forwarder-based 3PLs
These companies offer freight forwarding and customs brokerage services to manage international shipments.
Forward-based third-party logistics (3PL) is a type of logistics service that involves strategically placing inventory and distribution centers close to the end customer in order to improve delivery times and reduce transportation costs.
In a forward-based 3PL model, a 3PL provider establishes warehousing and distribution centers in key locations near major population centers or transportation hubs. This allows them to quickly fulfill orders and deliver products to customers in a timely and cost-effective manner.
For example, a company that sells products online may choose to partner with a forward-based 3PL provider to store its inventory in warehouses located in different regions across the country. This would enable them to quickly ship products to customers in each region, reducing transit times and shipping costs.
Financial-based 3PLs
Third-party logistics (3PL) providers specializing in financial and information services are often preferred by larger e-commerce companies as they offer a range of services that optimize a company’s logistics network.
These 3PLs provide various services such as accounting, cost control, freight forwarding, inventory tracking, and management, as well as other similar functions. They use advanced software and technology to manage complex logistics operations, ensuring that the company’s supply chain runs smoothly and efficiently.
Some larger 3PL providers offer comprehensive services in all of the above areas for their clients, providing a one-stop shop for all their logistics needs. By working with a financial and information 3PL provider, companies can benefit from increased visibility, cost savings, and improved accuracy in managing their logistics operations.
Benefits of Third-Party Logistics in Supply Chain Management
Third-party logistics (3PL) refers to the outsourcing of logistics and supply chain management activities to a specialized company. There are several benefits of using third-party logistics in supply chain management, including:
Cost savings
3PL providers have the expertise and resources to optimize logistics operations, which can result in cost savings for businesses. These cost savings come from reduced transportation costs, lower inventory carrying costs, and more efficient supply chain operations.
Improved focus on core business activities
By outsourcing logistics and supply chain management activities, businesses can focus on their core competencies and key business activities. This allows them to devote more time and resources to areas such as product development, marketing, and sales.
Scalability
3PL providers can offer businesses scalable logistics solutions that can adjust to their changing needs. This means that businesses can easily expand or contract their logistics operations as demand fluctuates without having to make significant investments in infrastructure.
Access to technology and expertise
3PL providers have access to the latest technology and expertise in logistics and supply chain management. This allows businesses to leverage these resources without having to make significant investments in technology or hire specialized staff.
Improved customer service
By outsourcing logistics and supply chain management activities, businesses can improve their customer service. 3PL providers can offer faster delivery times, better tracking and visibility of shipments, and other services that can improve customer satisfaction.
Overall, the use of third-party logistics can provide significant benefits for businesses looking to optimize their supply chain operations, reduce costs, and improve customer service.
Risk management:
3PL providers can help businesses manage risks in their supply chain, including disruptions due to natural disasters, transportation delays, and other unforeseen events. By having a third-party logistics provider, businesses can better manage these risks and ensure the continuity of their operations.
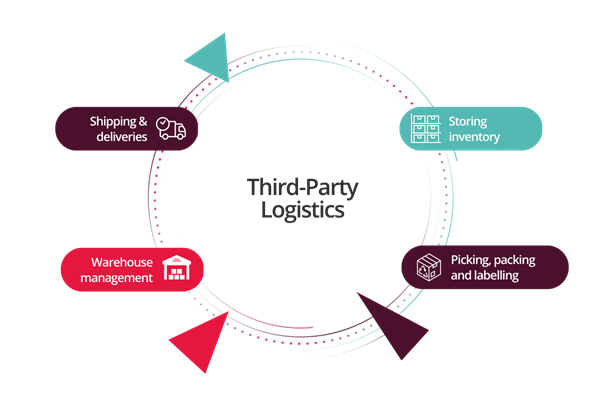
What Are the Responsibilities of a 3PL?
The responsibilities of a third-party logistics (3PL) provider can vary depending on the specific services that they offer and the agreement they have with their clients. However, some of the typical responsibilities of a 3PL provider include:
Transportation management
3PL providers are responsible for managing the transportation of goods from one location to another. This includes selecting the appropriate mode of transportation, arranging for carriers, and tracking shipments.
Warehousing and distribution
3PL providers may be responsible for managing the storage, handling, and distribution of goods in warehouses and distribution centers. This includes receiving and inspecting goods, managing inventory levels, and fulfilling orders.
Inventory management
3PL providers are responsible for managing inventory levels to ensure that there is enough stock to fulfill orders while minimizing excess inventory. This includes forecasting demand, replenishing inventory, and conducting regular inventory audits.
Order fulfillment
3PL providers are responsible for ensuring that orders are fulfilled accurately and on time. This includes picking and packing orders, managing shipping documentation, and coordinating with carriers to ensure timely delivery.
Customs brokerage and compliance
For companies that operate internationally, 3PL providers may be responsible for managing customs clearance and compliance with import and export regulations.
Technology and data management
3PL providers may offer technology solutions to help their clients manage their supply chain operations more efficiently. This can include transportation management systems (TMS), warehouse management systems (WMS), and other supply chain management tools.
Overall, the responsibilities of a 3PL provider are diverse and can encompass a wide range of services. The ultimate goal of a 3PL provider is to help their clients optimize their supply chain operations, reduce costs, and improve efficiency.
Also checkout the important of the best 3PL companies
How does 3PL pricing work?
The pricing structure of a third-party logistics (3PL) provider can vary depending on the specific services offered, the level of customization required, and the volume of business. However, there are a few common pricing models that are typically used in the industry:
Transactional pricing
This pricing model is based on a per-transaction fee, which is charged for each shipment, order, or service provided by the 3PL. This pricing model is often used for clients who have a low volume of transactions or who require ad-hoc services.
Fixed pricing
This pricing model is based on a fixed monthly or annual fee, which covers a set of predetermined services. This pricing model is often used for clients who have a predictable volume of business and who require a set of standard services.
Cost-plus pricing:
This pricing model is based on the cost of providing the service plus a markup or profit margin. This pricing model is often used for clients who require customized or complex services that are difficult to price upfront.
Performance-based pricing
This pricing model is based on achieving specific performance metrics or service levels. The 3PL provider is paid a base fee plus bonuses for achieving predetermined targets. This pricing model is often used for clients who require a high level of service quality and performance.
Shared savings pricing
This pricing model is based on sharing the cost savings achieved by the 3PL provider with the client. The 3PL provider is incentivized to find ways to reduce costs and improve efficiency to share the savings. This pricing model is often used for clients who have a high volume of business and who are looking to reduce costs.
Overall, the pricing structure of a 3PL provider can be complex and can depend on several factors. It is important for clients to work closely with their 3PL provider to understand the pricing structure and ensure that it aligns with their business needs and goals.
What’s the difference between 1LP, 3LP, and 4LP
There are three different ways a business can handle its logistics and shipping processes: 1PL, 3PL, and 4PL.
In a 1PL setup, the business does everything itself. They manage their own warehouse and shipping operations, from storing inventory to shipping products directly to customers.
In a 3PL setup, the business outsources its logistics operations to a third-party provider. The 3PL provider takes care of everything related to storing, managing, and shipping the business’s products.
In a 4PL setup, the business outsources all or most of its logistics operations to a fourth-party provider. This means that the 4PL provider manages everything related to the supply chain, and may even work with other third-party providers to handle logistics services.
Overall, the main difference between these setups is who is responsible for managing the logistics operations, and how much control the business has over the process.
Technologies in 3PL
In recent years, there have been significant technological advancements in the logistics industry, including shopping cart platforms, enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems, and electronic data interchange (EDI) connections with retailers. These technologies have made logistics operations more complex, and it can be difficult for businesses to manage them on their own.
A technology-focused 3PL provider can help businesses navigate these complexities by leveraging their expertise and in-house technology team to ensure that these systems are set up correctly and maintained. They can provide the necessary tools to give businesses a real-time look at their inventory and fulfillment processes, allowing them to make more informed decisions.
When evaluating a potential 3PL partner, it’s important for businesses to consider the tools and technical support that will be available to them. A 3PL provider with a strong focus on technology can offer significant benefits in terms of efficiency, accuracy, and cost savings.
Expedited Shipping
- 73% of shoppers expect affordable and quick deliveries.
- 44% of online shoppers abandon their carts due to shipping and handling costs.
- 24% of customers cancel an order due to slow shipping.
To meet customer demands for expedited shipping and grow sales, businesses can consider outsourcing their shipping and fulfillment needs to a third-party logistics provider (3PL). By doing so, businesses can access discounts, shipping options, and advanced technology that may not be available if they handle their orders in-house.
An established 3PL will have a network of warehouses, advanced technology, and trained staff to execute quick and efficient delivery. They can keep track of a package from start to end and overcome any shipping issues that may arise. Plus, their reputation depends on delivering packages to the right place, at the right time, and in proper condition.
Distributed Inventory
Most 3PLs have multiple locations that are strategically spread throughout the country or globally. This ensures the quickest and most cost-effective process to deliver products from the seller to the consumer. By automating the order process, a 3PL can ensure that products leave from the right locations, delivering optimal results for timeliness and shipping costs.
Choosing the right 3PL with the best locations and distribution points can maximize the benefits for a seller. Depending on a seller’s individual needs, having products located at multiple fulfillment facilities could facilitate a much quicker delivery process at a fraction of the cost compared to having all their products at one facility.