Cash-to-Cash Cycle : what it is ?
Every business owner knows that cash is king. However, it’s not just about having cash in hand. The management of cash from the moment it is invested in raw materials to the moment it is collected from clients is critical to a company’s success. This is where the Cash-to-Cash Cycle comes in. In this article, we will discuss what it is, how to calculate it, and how businesses can optimize it.
What is the Cash to Cash Cycle?

The Cash-to-Cash Cycle is a critical metric that measures the efficiency of a company’s cash management system. It is the time it takes for a company to convert its investment made in raw materials into cash received from customers.
The cycle starts with the purchase of raw materials and ends when the company receives payment from its customers. It takes into account the entire production process, including ordering of raw materials, manufacturing of goods, inventory holding, and collection of payments. The Cash-to-Cash Cycle is a vital metric for businesses of all sizes, as it provides insight into how well a company is managing its cash flow.
For example, a company that has a long Cash-to-Cash Cycle may struggle with cash flow issues, as it takes longer for them to receive payment from customers. This delay can cause problems with paying suppliers and employees, which can ultimately impact the company’s bottom line.
On the other hand, a company with a short Cash-to-Cash Cycle can quickly convert its investment into cash, allowing them to reinvest that cash into the business or pay off debts.
Several factors can impact a company’s Cash-to-Cash Cycle, including the efficiency of their supply chain, the quality of their inventory management, and the effectiveness of their accounts receivable process. By analyzing this metric, businesses can identify areas for improvement and implement strategies to optimize their cash flow.
Overall, the Cash-to-Cash Cycle is a crucial metric for any business looking to improve its cash management system and ensure its long-term success.
How to Calculate the Cash-to-Cash Cycle

The Cash-to-Cash Cycle is an important metric that measures the amount of time it takes for a company to convert its investments in inventory and other resources into cash. It is a critical financial metric that helps businesses understand their cash flow and liquidity. The calculation of the Cash-to-Cash Cycle is not complicated, and it involves the following formula:
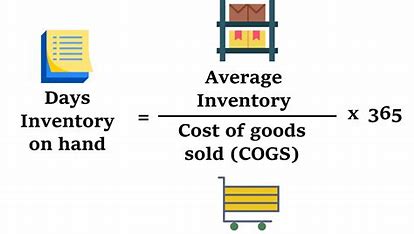
- Days Inventory Outstanding (DIO) = (Average Inventory / Cost of Goods Sold) x 365 days
- Days Sales Outstanding (DSO) = (Average Accounts Receivable / Annual Credit Sales) x 365 days
- Days Payable Outstanding (DPO) = (Average Accounts Payable / Cost of Goods Sold) x 365 days
- Cash-to-Cash Cycle = DIO + DSO – DPO
It is important for businesses to track their Cash-to-Cash Cycle regularly and make adjustments as needed to improve their cash flow and overall financial health.
The Formula for the Cash to Cash Conversion Cycle
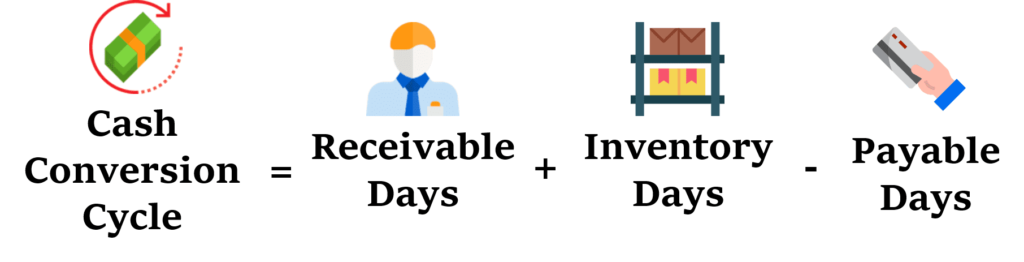
The Cash Conversion Cycle is a crucial metric for measuring a company’s efficiency in managing its working capital. It represents the time it takes for a company to convert its investment in raw materials into cash received from customers. The formula for calculating the Cash Conversion Cycle is simple:
Cash Conversion Cycle = Days Inventory Outstanding + Days Sales Outstanding – Days Payable Outstanding
The Days Inventory Outstanding (DIO) represents the average number of days it takes for a company to sell its inventory. This includes the time it takes for raw materials to be converted into finished goods and for the finished goods to be sold. A high DIO indicates that a company is holding onto inventory for too long, which ties up cash and reduces profitability.
The Days Sales Outstanding (DSO) represents the average number of days it takes for a company to collect payment from its customers. This includes the time it takes for the company to invoice its customers and for the customers to pay. A high DSO indicates that a company is not collecting cash from its customers quickly enough, which can lead to cash flow problems.
The Days Payable Outstanding (DPO) represents the average number of days it takes for a company to pay its suppliers. This includes the time it takes for the company to receive an invoice from its suppliers and for the company to pay the invoice. A high DPO indicates that a company is taking too long to pay its suppliers, which can damage supplier relationships and lead to supply chain disruptions.
By subtracting the DPO from the sum of the DIO and DSO, we get the Cash Conversion Cycle. A shorter Cash Conversion Cycle indicates that a company is managing its working capital more efficiently, which can improve profitability and cash flow.
It’s important to note that the Cash Conversion Cycle formula can vary depending on the industry and the company’s specific operations. For example, a company that operates on a cash basis may not have a DSO component, while a company that relies heavily on inventory may have a higher DIO component.
In conclusion, the Cash Conversion Cycle is a key metric for measuring a company’s efficiency in managing its working capital. By understanding the formula and the components that make it up, companies can identify areas for improvement and work towards a more efficient cash conversion cycle.
What does the Cash Conversion Cycle say about a company’s management?
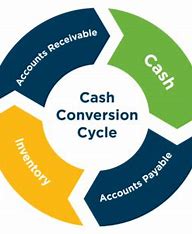
The Cash Conversion Cycle is a financial metric that measures the time it takes for a company to convert its inventory into cash. It is an essential tool for evaluating a company’s financial health and management style. The Cash Conversion Cycle is calculated by adding the number of days it takes for a company to sell its inventory, the number of days it takes to collect payment from customers, and the number of days it takes to pay suppliers.
A long Cash Conversion Cycle suggests that a company is taking longer to convert its inventory into cash, which can lead to cash flow problems, reduced profitability, and potentially put the business at risk. The longer it takes for a company to receive payment from customers and pay suppliers, the more cash it needs to keep its operations running. This can lead to a strain on the company’s cash reserves and limit its ability to invest in growth opportunities.
On the other hand, a short Cash Conversion Cycle indicates that a company is efficiently managing its cash flow, which can lead to increased profitability and growth. A company that can quickly convert its inventory into cash and collect payment from customers can reinvest that cash into its operations, pay suppliers promptly, and take advantage of growth opportunities.
It’s important to note that the Cash Conversion Cycle can vary widely between industries. For example, a company that sells high-end luxury goods may have a longer Cash Conversion Cycle than a company that sells low-cost consumer goods. This is because customers may take longer to pay for high-end goods, and the company may need to hold onto inventory for longer periods.
In conclusion, the Cash Conversion Cycle is a crucial metric for evaluating a company’s financial health and management style. A long Cash Conversion Cycle can indicate potential cash flow problems, reduced profitability, and limited growth opportunities. A short Cash Conversion Cycle, on the other hand, can suggest that a company is efficiently managing its cash flow and poised for growth.
Reducing the Cash-to-Cash Cycle Time

Photo by Tima Miroshnichenko
Reducing the Cash-to-Cash Cycle time is crucial for businesses that want to improve their bottom line and become more profitable. One effective way to reduce the cycle time is to evaluate the company’s inventory holding periods and shorten them. This can be achieved by improving the production process and ensuring that only the required inventory is kept on hand. An efficient inventory management system can also help in achieving this goal.
Optimizing the Cash-to-Cash Cycle
Optimizing the Cash-to-Cash Cycle involves taking a close look at every step in the production process, from ordering raw materials to collecting payment from customers. Companies that want to optimize their Cash-to-Cash Cycle need to streamline their business processes, improve communication with suppliers and customers, and use automation tools wherever possible. By doing so, businesses can reduce errors, reduce the time it takes to complete tasks, and optimize cash flow.
Automating the Cash-to-Cash Cycle
Automation tools can help businesses streamline their production process and optimize cash flow. For instance, automated invoicing and payment processing can speed up the collection of payments, while automated inventory monitoring can help businesses keep track of their inventory levels and order raw materials in time. Automation can also reduce errors and improve productivity, which can lead to an optimized Cash-to-Cash Cycle.
How does inventory turnover affect the cash conversion cycle?
Inventory turnover refers to the number of times a company sells and replaces its inventory over a specific period. A higher inventory turnover means a shorter Cash-to-Cash Cycle since the company is selling its goods quickly. On the other hand, a low inventory turnover means that the goods are taking a longer time to get to the market, leading to an extended Cash-to-Cash Cycle. Inventory turnover should be a key focus for businesses that want to improve their cash flow.
How the Cash to Cash Cycle is Used
The Cash-to-Cash Cycle is an essential metric that businesses use to evaluate their cash management processes. By measuring the time it takes for cash to flow through a business, companies can identify areas of improvement and make the necessary changes to optimize their cash flow. Whether it’s by reducing inventory holding periods, automating business processes, or improving communication with customers and suppliers, optimizing the Cash-to-Cash Cycle is crucial for business success.
Why is the Cash-to-Cash Cycle important?
The Cash-to-Cash Cycle is crucial because it directly impacts a company’s liquidity and working capital. By understanding how long it takes to convert investments into cash, businesses can optimize their operations and cash flow management to reduce the time between expenditure and revenue collection. A shorter cash-to-cash cycle allows for better financial stability, improved profitability, and increased reinvestment opportunities.