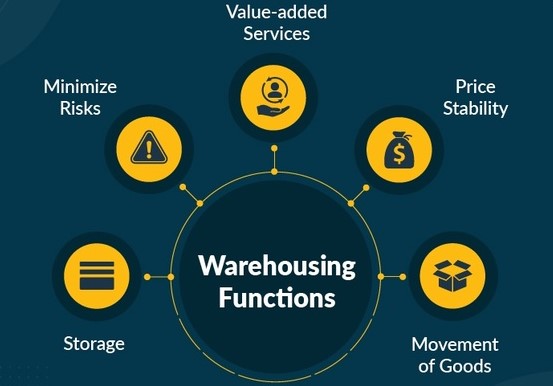
Warehouse management is the process of overseeing and optimizing the operations of a warehouse, including receiving, storing, and shipping goods. Effective warehouse management involves utilizing a variety of techniques and tools to maximize efficiency and accuracy, minimize costs, and ensure customer satisfaction.
Warehouse management challenges pose a significant threat to the efficiency and productivity of warehouses, hindering the workflow and potentially damaging the overall operations. Warehouses are complex systems that rely on various interdependent processes to effectively serve customers. Given recent events, warehouses must adapt to changing business dynamics to remain profitable while meeting customer demands.
Top 10 Warehouse Management Challenges
1. Inventory Management
- Order Fulfillment:
Inventory Management: Managing inventory levels effectively to avoid stockouts and overstocking, and ensuring that inventory accuracy is maintained. Inventory management is the process of overseeing the flow of goods into and out of a company’s inventory. Effective inventory management involves managing inventory levels in such a way that stockouts and overstocking are avoided, and inventory accuracy is maintained.
2. Labor Management
labor management is the process of organizing and scheduling labor resources in an efficient and effective manner. Effective labor management involves ensuring employees are properly trained and motivated, avoiding high employee turnover rates, and optimizing labor costs.
3. Space Utilization
space utilization is the process of optimizing the use of warehouse space to increase efficiency and productivity. Effective space utilization involves maximizing the use of available space, ensuring that the layout and design of the warehouse are conducive to efficient and effective operations, and minimizing waste..
4. order fulfillment
Meeting customer demand and delivering products on time is critical to the success of any warehouse operation. However, order fulfillment can be challenging due to various factors such as order complexity, order volume, and lead times.
5. Technology Integration
Warehouse managers are constantly looking for ways to improve efficiency, accuracy, and productivity in their operations. One of the most effective ways to achieve these goals is through the integration of technology into their warehouse management systems. However, this can be a challenge for warehouse managers, especially if they are not familiar with the latest technologies.
6. Regulatory Compliance
Ensuring compliance with regulations and standards related to safety, security, and environmental protection. Regulatory compliance is an essential aspect of warehouse management. Ensuring compliance with regulations and standards related to safety, security, and environmental protection is crucial for protecting employees, customers, and the environment. Failure to comply with regulations can result in fines, legal action, and damage to a company’s reputation.
7. Seasonal Demands
Managing seasonal fluctuations in demand and adapting operations to meet changing requirements. Seasonal demands can have a significant impact on warehouse operations. Managing seasonal fluctuations in demand requires warehouse managers to adapt their operations to meet changing requirements, which can be challenging.
8. Supplier Management
Managing relationships with suppliers to ensure timely and accurate deliveries of goods, and maintaining an accurate record of inventory levels.
9. Transportation and logistics management
Transportation and logistics management is the process of planning, implementing, and controlling the movement of goods and services from one location to another.
10 Risk Management
Identifying and mitigating risks related to warehouse operations, such as accidents, theft, and natural disasters, to protect employees and assets. Risk management is the process of identifying potential risks that could affect warehouse operations and taking measures to mitigate them. Some common risks related to warehouse operations include accidents, theft, and natural disasters. By identifying and mitigating risks, warehouse managers can protect employees and assets.
Also checkout the importance of the Warehouse Management Systems
Inventory Inaccuracy
Inventory inaccuracy refers to the discrepancies between the physical inventory count and the inventory records in a business system. When the actual inventory count doesn’t match the recorded inventory, it can lead to issues such as stockouts, overstocking, excess inventory, order fulfillment delays, and ultimately, financial losses.
There are various reasons why inventory inaccuracy can occur, including human error, theft, damage or loss of inventory, system glitches or failures, and inefficient Inventory Management processes. It can be particularly challenging for businesses that have a large inventory or deal with a high volume of sales.
To mitigate inventory inaccuracy, businesses can adopt best practices such as implementing automated inventory management systems, conducting regular physical inventory counts, using barcoding or RFID technology to track inventory movements, and training employees on proper inventory handling and management procedures. Additionally, having a well-planned inventory control strategy can help businesses improve accuracy and optimize their inventory levels.
Having a well-planned inventory control strategy can also help businesses improve accuracy and optimize their inventory levels. This strategy should include setting up inventory control policies and procedures, determining optimal inventory levels, and regularly monitoring and analyzing inventory performance to identify and address any issues. By implementing these measures, businesses can significantly reduce inventory inaccuracy, improve operational efficiency, and increase profitability.
poor warehouse layout
A poor warehouse layout refers to a situation where the design and organization of a warehouse do not optimize the use of available space, hinder the movement of goods,or impede productivity. A poorly designed warehouse layout can lead to a wide range of problems, such as inefficient use of space, increased labor costs, delays in product movement, reduced storage capacity, and increased safety risks.
There are several reasons why a warehouse layout may be poor. One common cause is the lack of planning and foresight when designing the warehouse, resulting in a layout that does not meet the current or future needs of the business. Inadequate warehouse management and poor inventory control can also contribute to a poor layout, as products may be placed haphazardly, without considering the optimal flow of goods.
- Analyze the warehouse: Identify areas where the warehouse is inefficient and the root causes of the inefficiencies.
- Review product storage: Review the product storage and picking methods used, such as FIFO or LIFO, and make necessary changes to improve efficiency.
- Optimize space: Make use of vertical space by adding racks and shelving systems, and identify any areas where space can be optimized.
- Implement technology: Implement technologies such as barcode scanning, RFID, and warehouse management systems to streamline operations and improve accuracy.
By optimizing the warehouse layout, businesses can improve the utilization of available space, reduce costs, improve safety, and enhance overall productivity.
Excessive spending on labor
Excessive spending on labor refers to a situation where a business is spending more than necessary on employee wages and other labor-related costs. This can have a significant impact on the company’s bottom line, resulting in reduced profitability and increased costs of goods sold.
There are several reasons why a business may be experiencing excessive spending on labor. One common cause is the overstaffing of employees, where more workers are employed than necessary to meet business demands. Inefficient labor practices, such as poor scheduling, lack of cross-training, and high employee turnover rates, can also contribute to excessive spending on labor.
- Optimize staffing levels: Conduct an analysis of the business’s workload and determine the optimal staffing levels necessary to meet business demands. Avoid overstaffing and hiring additional staff only when necessary.
- Implement labor management systems: Implement labor management systems that track employee productivity, monitor attendance, and manage scheduling to ensure that employees are utilized effectively.
- Invest in training: Cross-train employees to perform multiple tasks and skills, which can reduce the need for additional staff and increase productivity.
- Review wage rates and benefits: Review wage rates and benefits to ensure that they are competitive and aligned with industry standards. Consider offering incentives, such as bonuses or profit-sharing, to reward employees for their contributions.
By implementing these best practices, businesses can reduce labor costs, improve efficiency, and increase profitability.
Customer Expectations
Warehouse management faces several customer expectations challenges. Customers expect their orders to be fulfilled quickly, accurately, and efficiently, and failure to meet these expectations can result in lost sales, decreased customer satisfaction, and a negative impact on the business’s reputation. Some common customer expectation challenges in warehouse management include:
- Speed and Accuracy: Customers expect their orders to be fulfilled quickly and accurately. This requires warehouses to have efficient picking, packing, and shipping processes in place to ensure that orders are fulfilled in a timely and accurate manner.
- Order Tracking: Customers expect real-time visibility into the status of their orders, including tracking information and estimated delivery dates. Warehouses need to have systems in place to provide customers with accurate and up-to-date information about their orders.
- Returns Management: Customers expect a simple and hassle-free returns process. Warehouses need to have efficient returns management processes in place to handle returns quickly and accurately.
- Communication: Customers expect clear and prompt communication from the warehouse regarding order status, shipping updates, and any issues that may arise. Warehouses need to have effective communication channels in place to keep customers informed throughout the order fulfillment process.
To meet these customer expectations, warehouses can implement best practices such as efficient picking and packing processes, accurate inventory management, and effective communication channels. Investing in technology such as warehouse management systems, order tracking software, and automated material handling equipment can also help warehouses improve efficiency and meet customer expectations.
